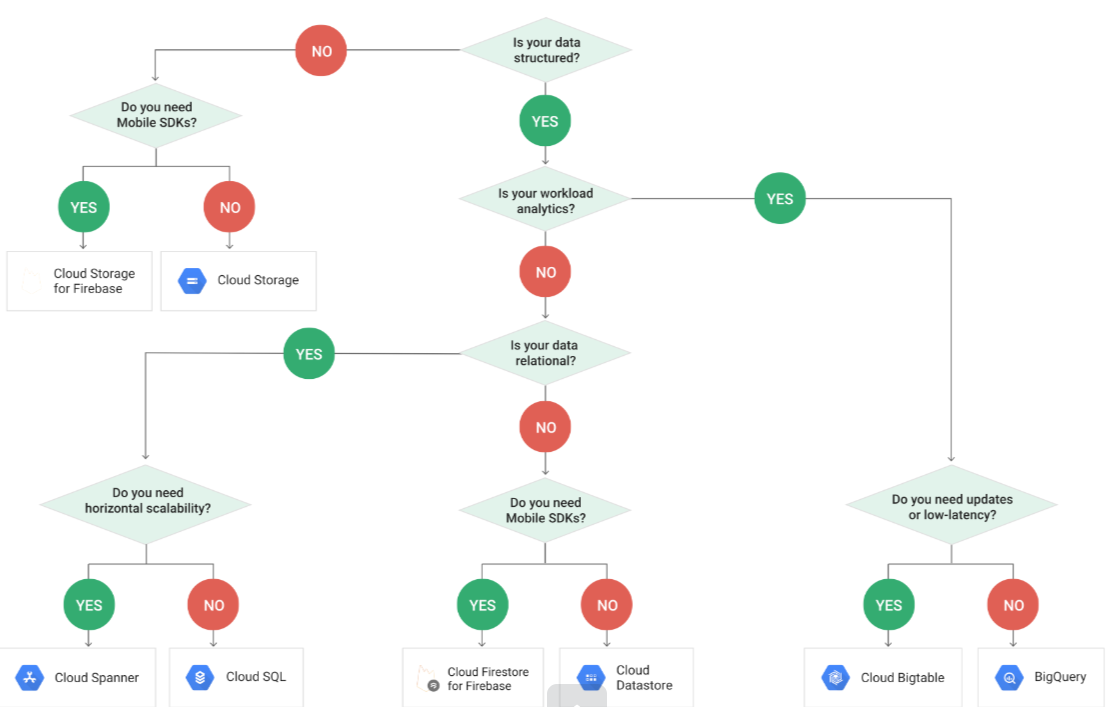
Database Types
Relational database
- SQL
- ACID ( Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability)
- Transactional
- Examples
- Mysql, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL
- Pros
- Standard, consistent, reliable, data integrity
- Cons
- Poor scaling, not fast, not good for semi-structured data
“Consistency and Reliability over Performance”
Non-Relational Database
- Non-structured
- Some have ACID (Datastore)
- Examples
- Redis, MongoDB, Cassandra, HBase, Bigtable, RavenDB
- Pros
- Scalable, High Performance, Not Structure-Limited
- Cons
- Consistency, Data Integrity
“Performance over Consistency”
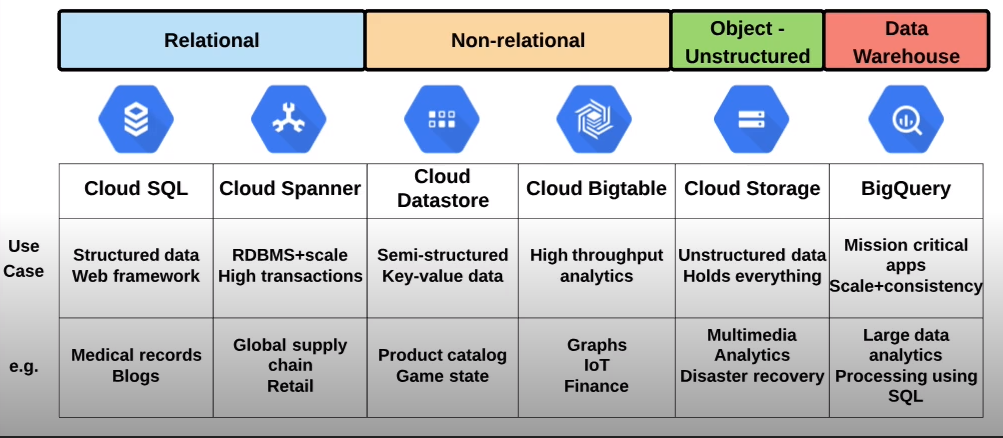
How to choose the right storage