We can run virtual machines by using of Compute Engine
VPC Network
Virtual Private Cloud: it connects your GCP resources to each other and to the internet.
Google Cloud VPC networks are global, but the subnets are regional
In the example below, us-east1-b and us-east1-c are on the same subnet but in different zones
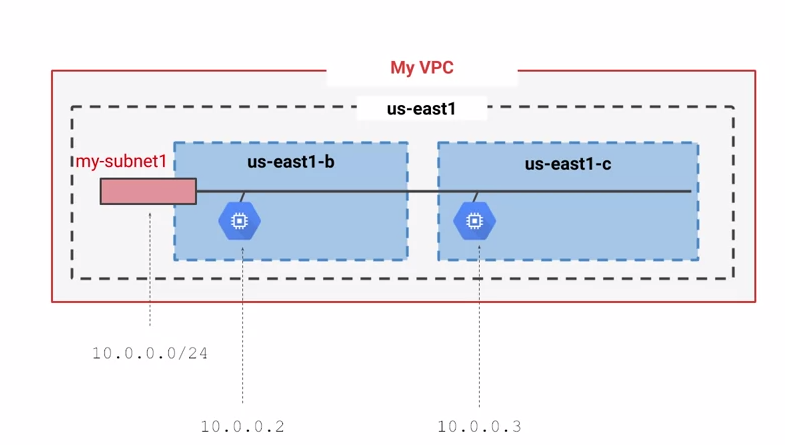
VPCs have routing tables, you can define firewall rules in terms of tags on compute engine.
VPC Peering: establish a peering relationship between projects
Shared VPC: you can use IAM to control
Cloud Load Balancing
Users get a single, global anycast IP address
Cloud CDN(Content Delivery Network)
Use Google’s globally distributed edge caches to cache content close to your users
Compute Engine
Create virtual machine by using of:
- GCP Console
- gcloud
You can run images of linux or windows servers.
You can configure memories and cpus of each VM, you can choose 2 kinds of storage: standard or SSD
You can choose a Preemptible VM to save money (the instance will terminate after 24 hours, it can be used for applications
distribute processes across multiple instances in a cluster or for test)
Scale up:
use big VMs for memory and compute-intensive applicationsScale out:
Use Autoscaling for resilient, scalable applications